Intestine related DMPK analysis using RepliGut® Planar Models
Verify your Caco-2 results using multiple donors and regions for reducing late-stage failures
Importance of intestinal contribution to DMPK
In vitro modeling of intestinal absorption plays a pivotal role in advancing preclinical drug development by bridging the gap between laboratory research and clinical application. Predictions of bioavailability derived from cell culture models serve to refine drug design, optimize formulations, and flag potential safety issues. The RepliGut® Planar model is the first intestinal epithelial model that accurately reflects human intestinal contribution to metabolism and transport in a format similar to Caco-2 cells, enabling scientists to further close the gap between in vitro and in vivo bioavailability prediction and reduce late-stage clinical failures.

BCS permeability classification in accordance with the ICH M9 guidance criteria

RepliGut® Planar- Jejunum distinguishes between high and low BCS classification drugs. Correlation between RepliGut® Planar-Jejunum Papp and human absorption. Dotted lines indicate threshold between high and low permeability drugs
RepliGut® Planar- Jejunum distinguishes between high and low BCS classification drugs. Fourteen (14) compounds were tested in accordance with ICH M9 guidance criteria for Papp and compared with known human fraction absorbed (Fa).
High Permeability
- Propranolol
- Antipyrene
- Metoprolol
- Desipramine
- Theophylline
- Carbamazepine
- Ketoprofen
Low Permeability
- Terbutaline
- Atenolol
- Enalapril Maleate
- Lisinopril
- Nadolol
- Ranitidine
- Furosemide
Correlation of Papp measurements to Caco-2

Comparison of passive permeability between RepliGut® Planar-Jejunum and Caco-2 cells. The apparent permeability of 14 drugs showed a strong correlation, with an R² value of 0.83.
How RepliGut® Planar compares
Ensuring accuracy in intestinal absorption modeling necessitates the presence and functionality of pertinent influx and efflux transporters along with metabolic enzymes. While Caco-2 cells have conventionally served as the benchmark cell culture model for in vitro absorption investigations, their fidelity to native human intestinal tissues is compromised by unregulated proliferation, physiologically inaccurate differentiation processes, and altered expression of drug-related transporters and enzymes, thereby impeding their reliability in mimicking in vivo drug absorption and metabolism.
Feature | Caco-2 Cells | RepliGut® Planar | In Vivo |
|---|---|---|---|
Human origin | |||
Polarized epithelial monolayer | |||
Multiple cell lineages | |||
Regional specificity maintained | |||
Interindividual variability | |||
Mucus excretion | |||
Phase I and II metabolism | |||
96-well format |
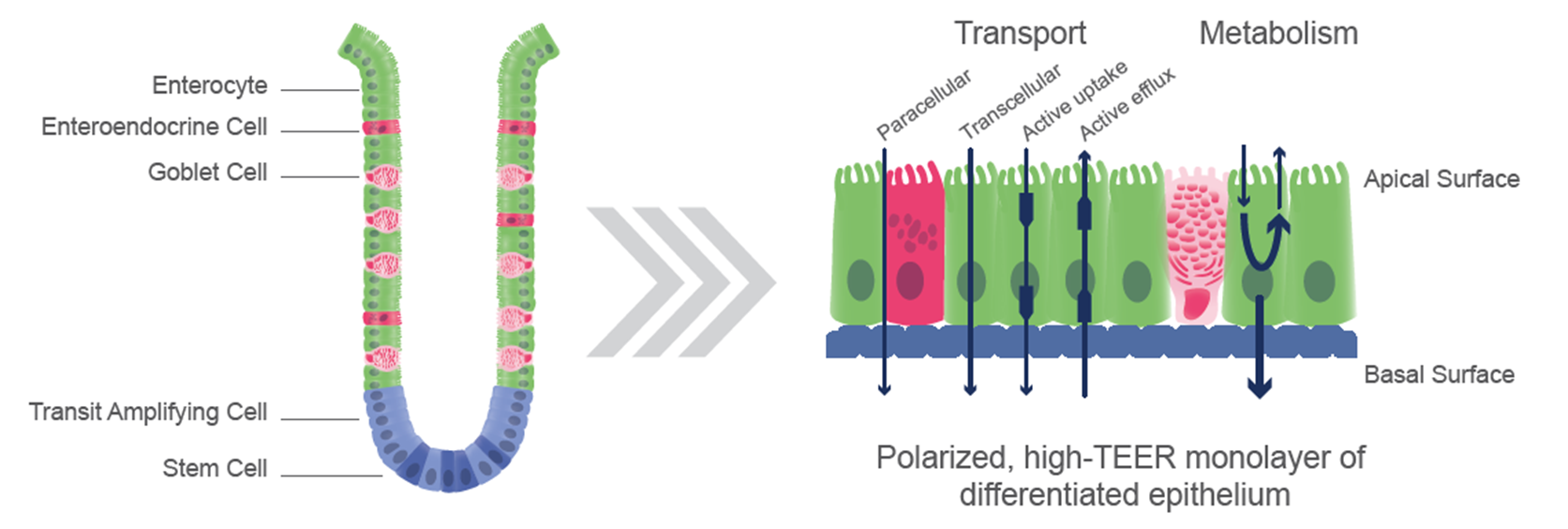
Unlike Caco-2 cells, RepliGut® models are comprised of multiple cell lineages found in the in vivo gut, which better reflect in vivo DMPK processes. The cell populations in RepliGut® models are confirmed to be ALP+, MUC2+ and CHGA+ positive and form a polarized monolayer with intact tight junctions.1 Furthermore, RepliGut® Jejunum models express more physiologically relevant levels of several genes encoding phase I and phase II metabolic enzymes reducing the chance of overpredicting bioavailability compared to Caco-2 cells
RepliGut® Models enable you to assess region-specific DMPK endpoints, from more than one donor, for a more thorough vetting of drug candidate bioavailability.
Capabilities Summary
Click each to read more
Apparent permeability (Papp) and efflux ratios
Human jejunum epithelial stem cells are cultured and differentiated on semi-permeable membrane inserts in a 96-well plate to facilitate access to both the apical and basal sides of the cell monolayer. Test compounds are introduced into either compartment to assess their transport in both directions. Accurate mass spectrometry analysis of compound concentrations in each compartment allows for the calculation of permeability (Papp) and efflux ratios. Controls such as atenolol and propranolol, representing low and high permeability respectively, can be included. Additionally, transporter inhibitors can be applied to assess compound interactions with specific transporters. These assays are adaptable to specific research needs.
Typical study design | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cell Culture Timeline | 10-11 days | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Number of Replicates | Typically 3 wells per treatment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Incubation Time | Up to 120 min | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Incubation Buffer | HBSS + 10mM HEPES + 10mM Glucose, pH 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Barrier Integrity Assessment | Automated TEER using EVOM™ Auto (WPI) measured before and after compound incubation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Control Drugs | Atenolol and propranolol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Analysis Method | Accurate mass spectrometry measurement using LC/MS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data Readout | Papp (apparent permeability coefficient), Efflux ratio, TEER | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
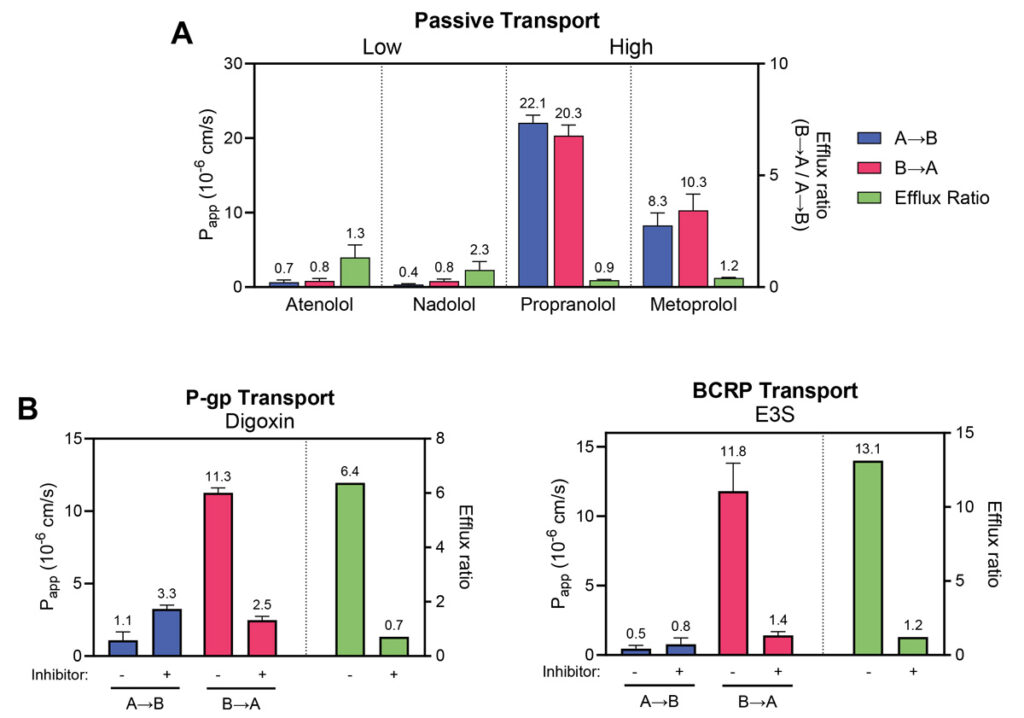
Permeability markers tested in RepliGut® Planar-Jejunum
Absorption Group | Drug | RepliGut® A→B Papp (10-6 cm/s) | Human Fraction Absorbed (Fa) |
|---|---|---|---|
High absorption (Fa ≥ 85%) | Antipyrine | 14.7 ±2.3 | 97% |
Metoprolol | 10.5 ±5.3 | 95% | |
Propranolol | 22.1 ±1.0 | 90% | |
Carbamazepine | 12.8 ±3.2 | 85% | |
Moderate absorption (Fa = 50 – 84%) | Ranitidine | 0.98 ±0.2 | 50% |
Atenolol | 0.97 ±0.9 | 50% | |
Low absorption (Fa < 50%) | Nadolol | 0.47 ±0.29 | 34% |
Lisinopril | 0.17 ±0.14 | 25% |
Absorption Group | Drug | Transporter | Efflux Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
Efflux Substrates | Antipyrine | P-gp | 12.5 ±5.8 |
Estrone-3-sulphate | BCRP | 30.7 ±14.4 |
Intestinal contribution to metabolic stability
Human jejunum epithelial stem cells are cultured and differentiated on semi-permeable membrane inserts in a 96-well plate to facilitate access to both the apical and basal sides of the cell monolayer. Test compounds are introduced into either compartment to assess their transport in both directions. Accurate mass spectrometry analysis of compound concentrations in each compartment allows for the calculation of permeability (Papp) and efflux ratios. Controls such as atenolol and propranolol, representing low and high permeability respectively, can be included. Additionally, transporter inhibitors can be applied to assess compound interactions with specific transporters. These assays are adaptable to specific research needs.
Drug metabolism and transporter gene expression analysis
Transcriptomic analysis of RepliGut® Planar Systems can provide insights into gut-specific metabolic activity and potential for drug-drug interactions in the GI tract. We offer QuantiGene™ Plex Gene Expression Assays or TaqMan probe RT-PCR to provide targeted gene expression analysis to focus on the impact to your genes of interest. A reference RNAseq data set is available to confirm expression of your gene of interest in RepliGut® Planar- Jejunum.

Accurate mass spectrometry method development with quantitative or qualitative bioanalysis
Altis has partnered with BioAgilytix Labs to offer method development and bioanalysis using state of the art LC/MS instrumentation including a high-throughput SCIEX Echo® MS+ coupled to a SCIEX ZenoTOF 7600.
Comparisons between intestinal regions and donors
We have isolated epithelial stem cells from multiple intestinal regions obtained from multiple donors, allowing researchers to study colon or small intestine-specific metabolism and transport in demographically diverse backgrounds (e.g. age, sex, blood type). Our cryopreserved biobank enables the ability to work with the same donor as your project progresses or have a variety of donors to evaluate donor differences.

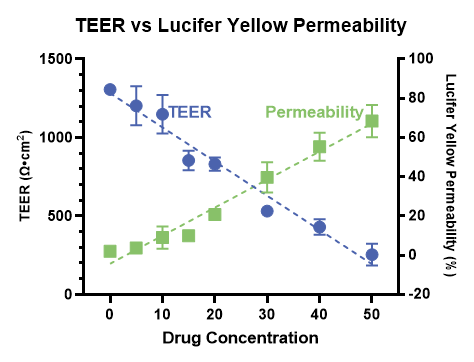
Companion barrier integrity monitoring
Accurate measurement of paracellular transport requires a consistently tight and intact cell culture barrier throughout the entire experiment. RepliGut® Planar barrier integrity is monitored in real time using Transepithelial Electrical Resistance (TEER). TEER is measured using the high-throughput and automated EVOM™ Auto (WPI) before and after compound incubation to ensure barrier integrity is not compromised.